Magnesium: Functions, Properties and Sources
Without magnesium, our body cannot function properly. This mineral is required for over 300 enzymatic reactions, hundreds of metabolic processes, and many other important body functions.
Magnesium is found throughout the body. Every cell in your body contains this mineral and needs it to function.
In addition, a deficiency of it can have a serious impact on your health.
However, despite the fact that it is found in a variety of foods, many people do not get enough of it.
Why is Magnesium Vital?
1. Is a cofactor for many enzymes:
o Converts food into energy
o Actively participates in protein metabolism
o Helps in the creation and repair of DNA and RNA
o Regulates signal transduction in nerve and muscle tissue
o Helps relax smooth muscle fibers
o Lowers blood pressure
2. Promotes better sleep
o Magnesium supplements are often used as a natural treatment for sleep problems such as insomnia.
o Magnesium regulates several neurotransmitters involved in the process of falling asleep.
o In one study of approximately 4,000 adults, magnesium intake was associated with improved sleep quality and duration
3. Helps fight depression
o Magnesium plays an important role in brain function and strongly influences our mood. A deficiency of magnesium in the body increases the risk of depression
4. Promotes heart health
o Magnesium plays an important role in maintaining heart health.
o Magnesium supplements lower blood pressure levels
5. Possesses anti-inflammatory properties
o A lack of magnesium in the body is directly linked to increased levels of inflammation.
o One clinical study concluded that Magnesium supplements reduced levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) , a marker of inflammation.
Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
What Causes Magnesium Deficiency?
o Diets poor in sources of magnesium
o Type 2 diabetes
o Digestive problems – such as Crohn’s disease
o Prolonged vomiting or diarrhea
o Kidney problems
o Long-term use of certain medications – such as diuretics or reflux medications
o Alcoholism
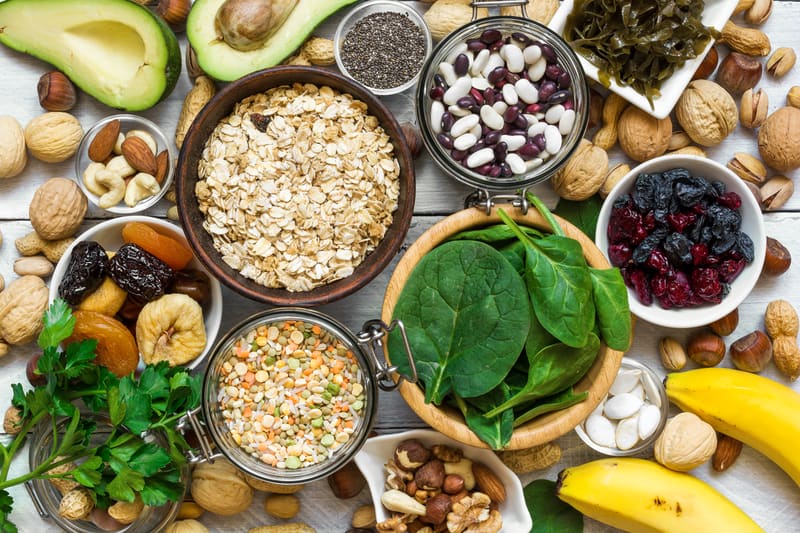
Top 7 Foods Rich in Magnesium
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Avacado
Avocados are an excellent source of magnesium. One medium avocado contains 58 mg of magnesium, which is 14% of the recommended daily allowance. In addition to magnesium, avocados are rich in potassium, B vitamins and vitamin K. Avocados are also a good source of fiber.

Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate is recognized as an excellent source of magnesium, containing 252.2 mg of magnesium per 100 g. In addition to this, dark chocolate is also high in iron, copper and manganese, and it contains prebiotic fiber that helps nourish beneficial bacteria in the gut.

Nuts - almonds, cashews and Brazil nuts.
Nuts are also a good source of fiber and Brazil nuts are rich in selenium. In addition, nuts have anti-inflammatory properties and are good for heart health. Adding nuts to your meals will keep you satiated for a long time. Just remember that you can't overdo it with nuts if you are in the process of losing weight. They are very caloric, so it is advisable to control their consumption.

Legumes
Legumes include lentils, beans, chickpeas, peas and soybeans. They are very rich in magnesium - 100 grams of cooked black beans contain 70 mg of magnesium. Legumes are also high in potassium and iron and are a major source of protein for vegetarians.

Tofu
Tofu - made by pressing soy milk into a soft white curd. There are 35 mg of magnesium in 100 grams of tofu. One serving of tofu also contains 10g of protein and good amounts of calcium, iron, manganese and selenium.

Bananas
Although bananas are best known for their high potassium content, they are also rich in magnesium: one large banana contains 37 mg of magnesium. In addition, bananas contain vitamin C, vitamin B6, manganese and fiber. When choosing bananas, you should take into account that the riper the banana, the more carbohydrates and sugar it contains. But in unripe bananas, a significant part of carbohydrates is resistant starch.

Leafy greens
Leafy greens - kale, spinach, leafy kale (collard greens) There are 79 mg of magnesium in 100 grams of spinach. In addition, leafy greens, are an excellent source of iron, manganese and vitamins A, C and K. Leafy greens also contain many beneficial plant compounds that help protect your cells from damage.
- By Yelena B
- One Comment



1 Comment
Leave a reply