9 Reasons to Include Zinc in Your Diet
- By Yelena B
- No Comments
Zinc is one of the most important trace elements. Since our body does not produce zinc on its own, because it is a chemical element and not a product of the body’s biosynthesis, humans need to get it from food or in the form of supplements.
The role of zinc cannot be overestimated. Zinc is found in every cell of the human body and without it our body would not be able to function properly.
Functions and Role of Zinc in the Body
- It is a component of many enzymes in the body (more than 300) involved in maintaining the structural integrity of proteins and in the regulation of gene expression;
- Influences cell growth, especially during cell reproduction and differentiation;
- Participates in the metabolism of:
o nucleic acids;
o proteins;
o vitamin A; - Maintains the concentration of vitamin E in the blood, including facilitating its absorption;
- Participates in the binding of certain hormones to appropriate receptors;
- Supports reproductive function;
- Participates:
o in hematopoiesis;
o in skin regeneration, sebum secretion;
o in the growth of nails, hair;
o in the detoxification function;
o in the work of taste and olfactory receptors - Boosts immunity;
Causes of Zinc Deficiency
- Insufficient intake with food;
- Absorption disorders (including vegetarianism);
- Increased need during pregnancy, breastfeeding;
- Chronic diseases of the liver, kidney and gastrointestinal tract
- Sickle cell anemia;
- Diabetes;
- Malignant neoplasms
- Post-surgical period, burns;
- Alcoholism;
- Medications (estrogens, corticosteroids, diuretics, etc.);
- Excessive intake of copper, lead, cadmium, mercury
- Worm invasions
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
- Disruption of carbohydrate metabolism;
- Risk of developing malignant neoplasms;
- Anemia;
- Loss of taste perception, sense of smell;
- Decrease in body weight;
- Slow healing of wounds, delamination of nails;
- Increased risk of developing diabetes;
- Prostate adenoma;
- Premature labor, birth of weakened babies, sterility in women;
- Allergic reactions;
- Accumulation of iron, copper, cadmium, lead in the body;
- Increased fatigue, irritability, memory and sleep disorders, hyperactivity, depression;
- Growth retardation;
- Dyspeptic disorders (diarrhea), appetite disorders;
- Sexual dysfunction: impotence and delayed puberty;
- Hair growth slowdown, dandruff, allopecia;
- Reproductive disorders;
- Eye damage (decreased visual acuity);
- Skin lesions (rashes);
- Reduced immunity;
Causes of Zinc Excess
- Excessive intake with food and water;
- Working in harmful working conditions (associated with zinc) and living in an environmentally unfriendly place;
- Use of medicines containing zinc (including zinc ointments);
- Metabolic disorders
Consequences of Zinc Excess
- Decreased immunity;
- Autoimmune reactions;
- Skin, hair, nail lesions;
- Dyspeptic disorders, stomach pain;
- Reduction of iron, copper in the body
- Hypofunction of prostate and pancreas, liver
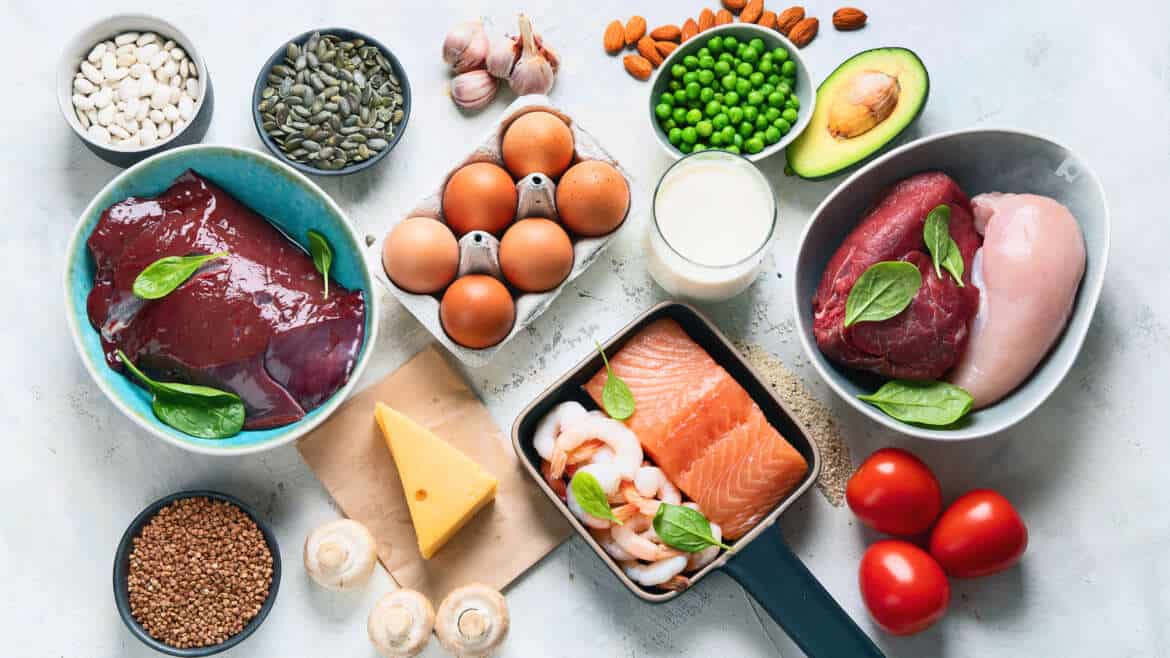
Foods Rich in Zinc

Shellfish: oysters, crab, lobster

Beef liver

Red meat

Offal

Seafood

Eggs

Whole Grains

Nuts and Seeds
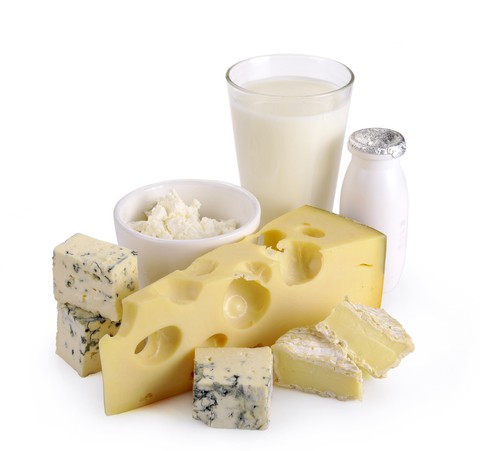

Dairy, escpecially cheese and milk that contain high amounts of bioavailable zinc

Dark Chocolate. Although, 3.5-ounce bar of 85% dark chocolate contains 3.31 mg of zinc, it is still no the best source of zinc as it uis high-calorie product.
Zinc and Skin
As far back as ancient Greek medical texts described zinc oxide as a therapeutic ointment for treating wounds. Today, zinc oxide is still a popular over-the-counter skin treatment. It protects against sunburn by reflecting and scattering ultraviolet rays so they do not penetrate the skin.
It is also used to treat inflamed skin areas such as burns, eczema, sores and diaper rashes. This compound forms a protective barrier on the surface of the skin, repelling moisture and allowing it to heal. It can also help enzymes break down damaged collagen tissues so that new ones can form.



Leave a reply